
One of the main issues impacting the reliability of LCA results is uncertainty (McKone et al. However, it is not fully accepted as such due to a perceived lack of robustness (Herrmann et al. Life cycle assessment (LCA) is intended as a quantitative decision support tool.
#Openlca capabilities software#
Improved practices should be encouraged and supported by peer-reviewers, editors, LCI databases and LCA software developers. More frequent and comprehensive reporting of uncertainty analysis is strongly recommended for published LCA studies. More standardized methods based upon context-specific data that strike the right balance between comprehensiveness and usability are, however, necessary in order to better account for both the shared and unique sources of uncertainty in attributional and consequential LCAs. There are hence no obvious barriers to quantifying parameter uncertainty in LCA studies. Moreover, uncertainty propagation for parameter uncertainty is supported by LCA modelling software.
stochastic) uncertainty data are widely available in LCI databases, and researchers should generally be able to define comparable uncertainty information for their primary data. Conclusionsĭata quality scores and inherent (i.e. Monte Carlo sampling was the most popular method used for propagating uncertainty results, regardless of LCA type. However, there are currently no widely applied methods to specifically account for these sources of uncertainty other than sensitivity analysis. allocation in attributional LCA versus the definition of market-mediated substitution scenarios in consequential LCA).
There are also sources of uncertainty specific to each kind of LCA-in particular related to the resolution of multi-functionality problems (i.e. Parameter uncertainty is most often reported, although the other types are considered equally important. There are many different sources of uncertainty in LCA, which can be classified as parameter, scenario or model uncertainty. Less than 20% of LCA studies published in the past five years reported any kind of uncertainty analysis. Observed practices were compared to best practice recommendations from methods papers, and additional recommendations were advanced. Common sources and methods for analysis of uncertainty in both attributional and consequential LCA were described, and their frequency of application evaluated. MethodsĪll relevant LCA methods papers as well as case studies (amounting to 2687 journal articles) published from 2014 to 2018 in the top seven journals publishing LCA studies were reviewed. This paper answers these questions based on a review of recent LCA studies and methods papers, and advances recommendations for improved practice. To date, little research has been reported regarding the comparative sources of uncertainty (and their relative importance) and how, or how commonly, they are quantified in attributional and consequential LCA. However, the large amount of uncertainty characteristic of LCA studies reduces confidence in results. Based on the LCA, areas for improvement of self-healing for geopolymers are also discussed.Life cycle assessment (LCA) is intended as a quantitative decision support tool. For microcapsule production, the solvent and the wall-forming monomer are the primary contributors to the assessed environmental impacts. The main contributors of the impacts are the alkali-activator production and the self-healing microcapsules. Self-healing geopolymer concrete was better in global warming potential but worse in other environmental impact categories than conventional OPC concrete. Life cycle impact assessment (LCIA) was carried out using the CML-IA methodology. The life-cycle inventory analysis (LCI) was done using databases in the OpenLCA software and literature.
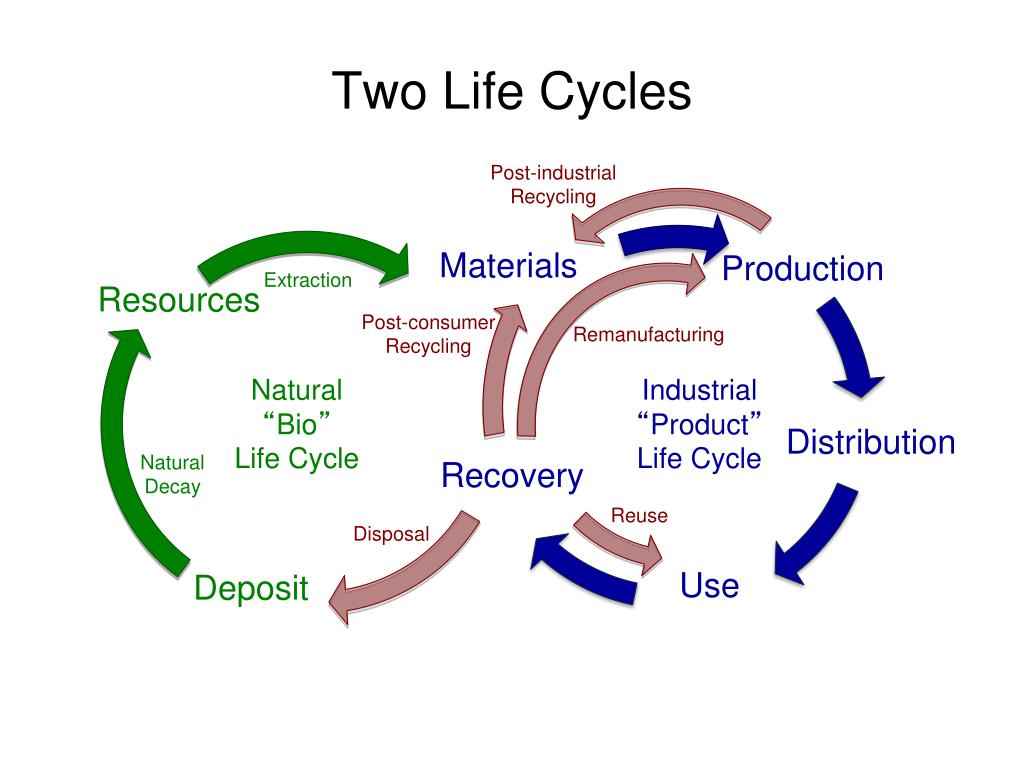
The system boundaries for this LCA focuses on a cradle-to-gate perspective. Life cycle assessment (LCA) of the self-healing geopolymer is important to justify its use from an environmental viewpoint. This study aims to quantify the expected additional environmental impacts brought about by adding self-healing microcapsules to geopolymers. The proposed self-healing method makes use of embedded microcapsules containing alkali-activators in geopolymer concrete. This study assesses the environmental impacts of a method for self-healing in geopolymers.
#Openlca capabilities crack#
However, studies have shown that geopolymers are more prone to crack propagation, which leads to reduced durability and serviceability. Geopolymers are a class of cementitious materials based on inorganic polymers, which are promising substitutes for ordinary Portland cement (OPC). Current construction developments are trending towards more sustainable practices with greener alternative materials such as geopolymers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
